LED and LCD are in today’s electronic screen display technology is widely used, the market is a variety of common LCD types, different technologies to form the LCD picture quality will be different, today we come together to briefly understand the common types of LCD technology on the market.
LCD Basics
LCD is commonly used in some modern electronic devices display screen, such as cell phones, tablets, computers, TVs. Its principle of action is to use the backlight to provide a light source for individual pixels arranged in a rectangular grid, and the light is refracted through the polarizer and liquid crystal material to achieve the purpose of the picture display.
What is the structure of an LCD?
An LCD consists of two transparent electrodes and a thin liquid crystal material. There is a polarizer on each side, and these two polarizers allow only light waves of a specific polarization to pass through, thus enabling the control of light.
LCDs usually use an LED as a backlight to make the pixels glow.
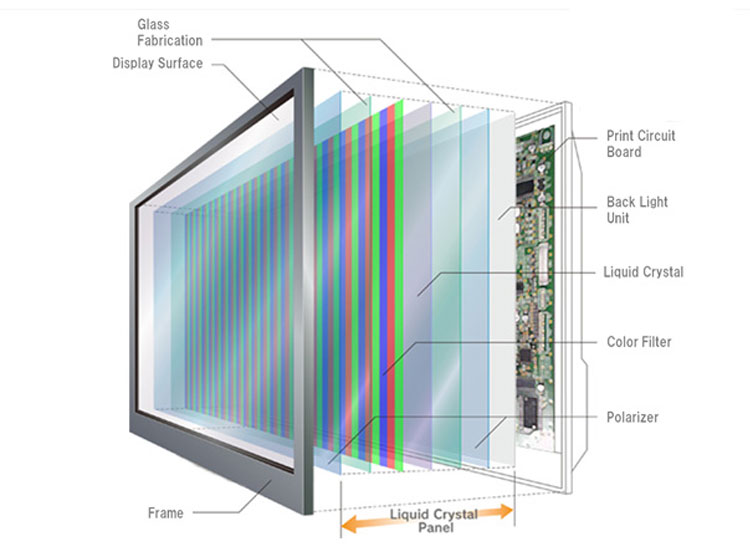
Types of LCDs
Distinguished by driving method:
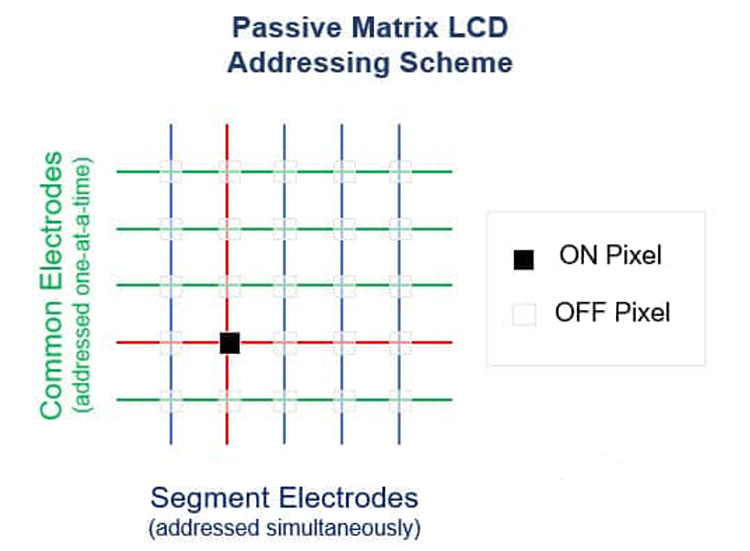
Passive Matrix Displays
The passive matrix is driven dynamically and is limited by the number of scanning electrodes.
Active Matrix Display
The driving method of active matrix is static driving, which is not limited by the number of scanning electrodes.
Distinguished by color:
Monochrome LCD
Monochrome LCDs do not have rich colors and have the advantage of simple construction and low energy consumption.
Multi-color LCD
Multi-color LCDs have rich colors and have the advantage of a wonderful visual experience.
Distinguished by the type of LCD technology:
According to the different forms of changes that occur when light enters the liquid crystal material, we usually categorize it into TN (Twisted Nematic), VA (Vertical Alignment), and IPS (In-Plane Switching), which are three common types on the market, and most of the LCD types have evolved on the basis of these three types.
TN – Twisted Nematic (90º twist)
TN LCD refers to charged nematic liquid crystal molecules arranged in a twisted 90º arrangement when the voltage is turned off. When the voltage is turned on, the TN liquid crystal molecules rearrange themselves, allowing some of the light to pass through the liquid crystal material to reach the polarizer and activate the pixels to form the picture.
HTN-Highly Twisted Nematic (110º~130º twist)
HTN LCD refers to charged nematic liquid crystal molecules that are aligned at 110º~130º when the voltage is off. When the voltage is turned on, the HTN liquid crystal molecules are rearranged to allow some light to pass through and form a picture.
STN-Super Twisted Nematic (240º~270º twist)
STN LCD refers to charged nematic liquid crystal molecules that are aligned at 240º~270º when the voltage is off. When the voltage is turned on, the STN liquid crystal molecules are rearranged to selectively transmit light waves by refraction and absorption, resulting in a picture.
FSTN-“Film Compensated” STN
FSTN LCD in the STN based on a new layer of compensation film, the principle of work and STN is basically the same, but the existence of compensation film to eliminate the STN dispersion problem, if the FSTN add RGB filters can become a full-color display.
DSTN-“double layer” STN
DSTN LCD is an advanced version of STN, the working principle is basically the same as STN, there are two STN modules, the screen can be divided into two, the refresh rate is twice as fast as STN, through the scanning of the two modules to achieve a clearer and more vivid picture.
VA(Vertical Alignment)
VA LCDs have crystals vertically aligned within two sheets of glass when not energized. When energized, the vertically aligned crystals are allowed to tilt, allowing light to pass through and form an image.
PLS-Plane to Line Conversion
PLS LCDs also allow light to pass through by crystal alignment and movement. On top of this, PLS uses a matrix of thin film transistors to control individual pixels, improving brightness and color accuracy.
TFT-Thin Film Transistor
TFT stands for thin-film transistor, and each pixel of a TFT LCD has a thin-film transistor attached to it. A TFT works by turning on an electric current that activates the transistor to contact the pixel, creating an image of excellent quality.
AFFS (Advanced Fringe Field Switching)
AFFS LCDs have the crystals aligned in a manner parallel to the glass substrate. When energized, the crystals rotate to allow light to pass through. AFFS has a high transmittance, which means that less light energy is absorbed within the liquid crystal layer, and more light energy is transmitted to the polarizer.
IPS(In-Plane Switching)
IPS LCD means that the crystals are aligned parallel to the glass substrate when not energized, and when energized, the crystals remain parallel to the plane of the glass and rotate to allow light to pass through, activating the pixels to form an image.
IPS has high image quality, wide viewing angles, and excellent performance, and it is one of the most common uses of LCD technology on the market today.
Differences between LED and LCD screens
Backlight Technology
- LCD: LCDs cannot emit light on their own, so they need LEDs or CCFLs as a backlight.
- LED: LEDs can emit light on their own, and each bead is a tiny light-emitting diode that emits light when an electric current is passed through it.
Contrast and black level
- LCD: LCD is a non-autonomous light source, the backlight source may have light leakage in the transmission process, the actual visual presentation of the contrast and black level will be lower than the LED screen.
- LED: LED screen can freely control the light emission of each LED lamp bead, therefore, it can produce higher contrast and deeper black, more vivid in visual presentation.
Energy Efficiency
- LCD: The backlight principle of LCD is such that the backlight is always on even when no light is being displayed, therefore LCD consumes more power.
- LED: LED is able to control each LED light individually, so that some LED lights on the screen that do not need color display are extinguished during playback to achieve energy saving.
Viewing Angle
- LCD: LCD’s viewing angle is more limited, in some unsuitable viewing angle to watch the LCD will have a very obvious color difference, and even can not watch the screen.
- LED: LED viewing angle are basically in the 160 degrees or so, a wider viewing angle, and LED screen can be freely assembled size, as the size increases, the viewing distance becomes farther, the appropriate viewing angle of the LED screen remains unchanged, but the appropriate viewing range becomes larger.
Environmental impact
- LCD: LCD backlighting technology consumes more energy, and the manufacturing materials may have heavy metals, a greater impact on the environment.
- LED: LED use process is very energy efficient, and manufacturing materials are environmentally friendly, less impact on the environment.
Brightness
- LCD: LCD non-autonomous light-emitting, light source through the filter and crystal material is absorbed part of the light energy, so the brightness is lower than the LED.
- LED: LED can freely control the brightness, the brightness can be produced according to the demand, can meet the indoor light viewing needs, can also meet the outdoor high lighting viewing needs.
Service life
- LCD: LCD has a shorter service life than LED screens due to the fact that the light-emitting principle requires the continuous movement of crystalline materials to create a suitable picture.
- LED: LEDs have no moving parts, are more stable in design and installation, and have a longer service life.
Conclusion
LCD different technology types of working principle leads to its use in life will be different, with the technology iteration, LCD different types of the various gaps are narrowing. LCD and LED screen are widely used in modern displays, both have their unique strengths, but in general in terms of brightness, energy consumption, and the service life of the LED screen is better than the LCD.



