LED display power consumption is one of the most critical factors people consider when purchasing an LED display. This is because it directly impacts the overall efficiency, durability, and operational costs of the display.
Whether you are planning to buy an LED display or have already purchased one, the following factors related to power consumption are essential to understand.
LED Display Power Consumption Explained
LED display power consumption refers to the electrical energy consumed by the screen during operation, typically measured in watts or kilowatt-hours.
This consumption is not fixed; various usage scenarios during operation yield different power consumption metrics.
LED Display Power Consumption Metrics
It’s important to know that LED display power consumption metrics are categorized into three types: maximum power consumption, black level power consumption, and standby power consumption. Below is an introduction to these three metrics:
Maximum Power Consumption
LED displays generate images or visual effects by illuminating diodes. During this process, the display adjusts the brightness of the diodes to varying levels.
Maximum power consumption refers to the LED display power consumption when all diodes operate at full power—that is, when the entire display is fully white and all diodes are at their maximum brightness.
Black Level Power Consumption
Black level power consumption refers to the energy used when your LED display shows no content.
Even when blank, the display’s components remain active, so this power consumption represents the baseline energy required by the electronic components themselves.
Standby Power Consumption
Standby power consumption refers to the energy used by the LED display in standby mode. Many products feature a standby state, commonly known as sleep mode.
In sleep mode, your LED display can significantly reduce energy consumption from component operation. While some components remain active in this mode, the power required is lower than black level power consumption.
Factors Affecting LED Display Power Consumption
As with any electronic device, the power consumption of an LED display is only a reference value. Actual power usage often varies due to numerous factors. Let’s explore some key factors influencing LED display power consumption.
Screen Size
Screen size is the primary factor affecting LED display power consumption. The size of an LED display directly correlates with the number of LED modules required.
Larger displays necessitate more LED modules, meaning more light-emitting diodes are needed to generate the image, thereby increasing power consumption.
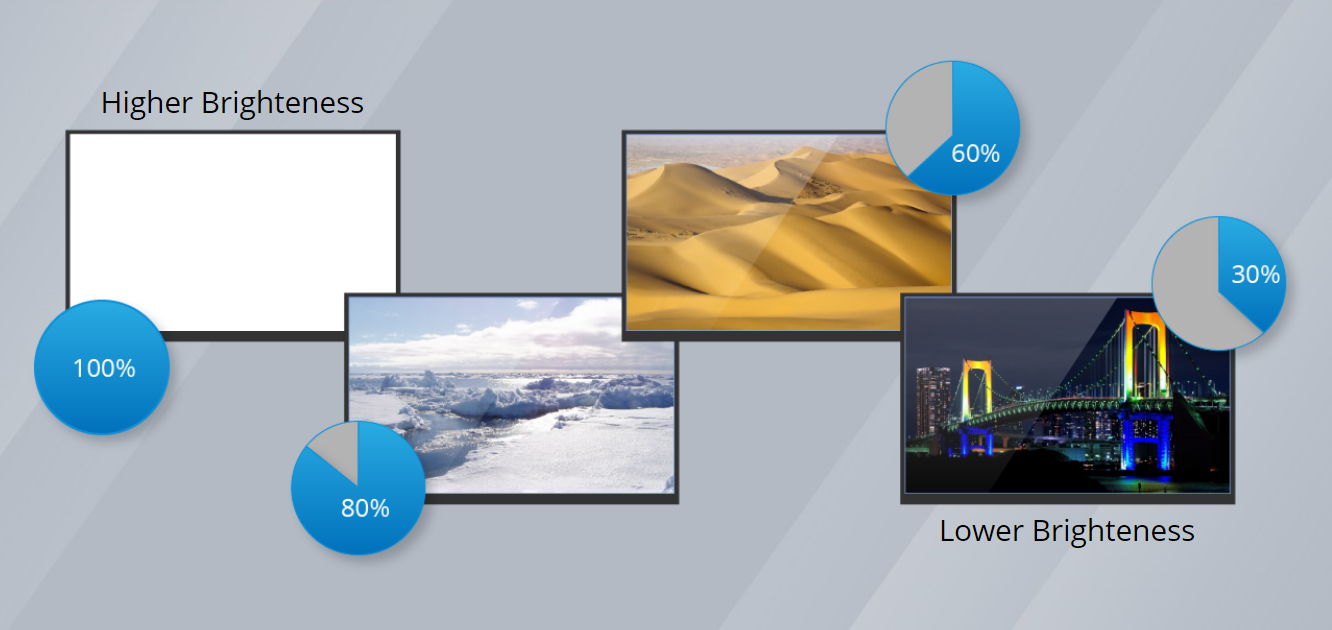
Brightness Level
The brightness level of an LED display directly correlates with its power consumption. Higher brightness demands greater power usage. Typically, outdoor LED displays require higher brightness levels than indoor displays, resulting in slightly higher power consumption.
LED displays equipped with light sensors can automatically adjust screen brightness to adapt to ambient light conditions, thereby reducing power consumption.

Pixel Pitch and Resolution
Pixel pitch also impacts power consumption. Smaller pixel pitch increases pixel density, requiring more LEDs to form higher-resolution images. Consequently, high-resolution displays consume slightly more power than low-resolution ones.
Refresh Rate
Refresh rate also affects LED display power consumption. This rate indicates how many times per second an image is refreshed on the display. Faster refresh rates produce better captured image quality.
Consequently, high-refresh-rate displays consume more power than low-refresh-rate ones.
Color
LED displays can present diverse content and colors. Did you know LED display power consumption is also linked to color? Theoretically, brighter colors demand higher power.
For instance, white consumes more power than black because achieving white requires more LEDs to produce greater luminosity.
Displayed Content
The content displayed on an LED screen also impacts LED display power consumption. When displaying only images or static text, power requirements are lower. Conversely, playing high-definition videos or animations consumes significantly more power.
LED Display Technology
When selecting LED display products, it’s important to understand that LED display technology also affects LED display power consumption.
Using screens from manufacturers with substandard technology may result in unreasonable power usage. Therefore, choosing the right LED display manufacturer is crucial.
We recommend selecting HOLA LED Manufacturer. Their products are backed by relevant certifications, so you needn’t worry about product quality or technical issues.
Their professional customer service team will address all after-sales concerns, providing comprehensive support. For any inquiries, feel free to call the contact number on the right.
LED Display Types
Different LED display types exhibit varying LED display power consumption levels. Outdoor and indoor LED displays face distinct environmental conditions, necessitating different considerations and consequently differing power requirements.
Generally, outdoor LED displays consume more power than indoor ones.
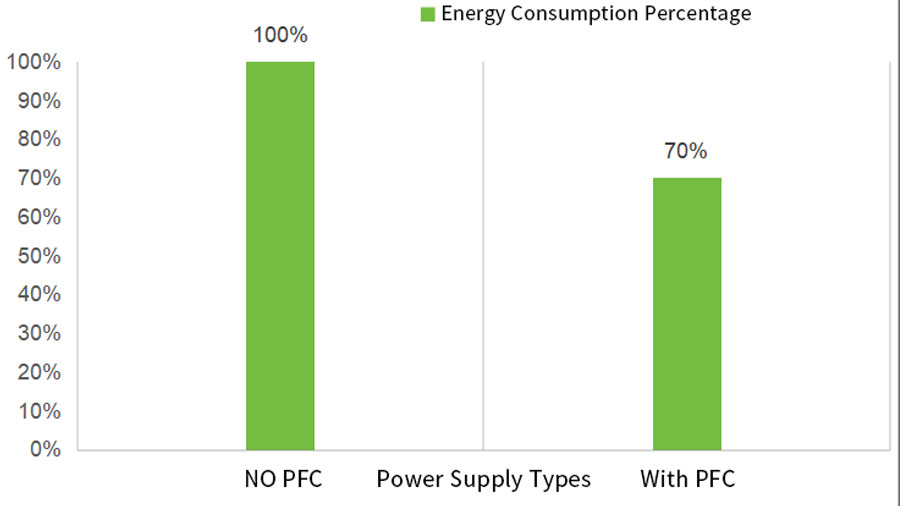
Power Supply and Efficiency
The quality of the power supply directly impacts the LED display power consumption. When selecting an LED display, check its rated power supply capacity.
A high-quality power supply efficiently converts AC to DC with minimal losses, thereby reducing power consumption to some extent.
Usage Duration
All electronic devices consume power during operation, and LED displays are no exception. Continuous operation consumes more power than intermittent use. Allowing appropriate rest periods for LED displays can consequently reduce LED display power consumption.
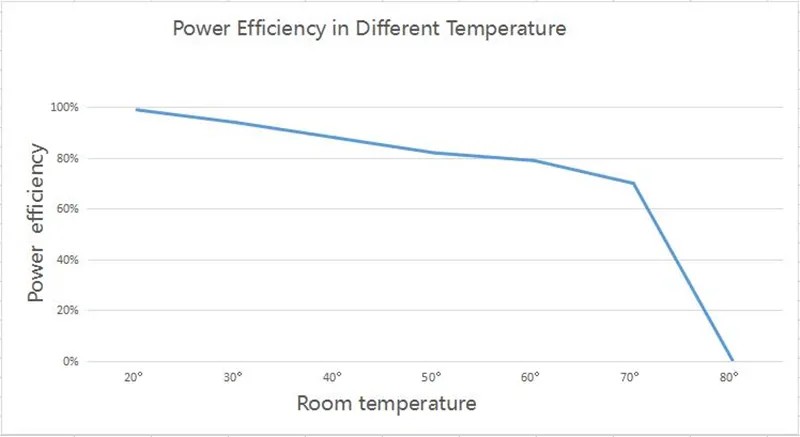
Environmental Conditions
Outdoor LED displays generally consume slightly more power than indoor ones, though LED display power consumption varies even among outdoor displays.
Compared to indoor use, high temperatures and humid environments cause increased power consumption. Similarly, adverse weather conditions may also slightly elevate power usage.
How to Calculate LED Display Power Consumption?
LED display power consumption is influenced by numerous factors. Therefore, when calculating power consumption, we can only determine its average value. This average serves as a reference and does not represent the final specific power consumption.
The calculation steps are as follows:
First, determine the screen area of the LED display:
- Calculate power density: Power density (W/m²) = Total power (W) / Area (m²).
Next, establish the brightness standard, typically expressed as a percentage:
- Formula: PC (Power consumption) = SA (Screen area) × PD (Power density) × B (Brightness)
Summary
Power consumption is a crucial factor to understand when purchasing an LED display, as it impacts your overall operating costs. However, due to multiple influencing factors, precise calculation is challenging.
You can mitigate unnecessary power usage by considering these variables.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can energy-efficient LED displays save power?
Energy-efficient LED displays utilize more advanced LED technology, reducing costs while being more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, thereby helping you save on power consumption.
Which consumes more power: LCD or LED displays?
LED displays employ more energy-efficient technology, emitting light directly and converting electrical energy into light energy more effectively.
LCD displays, however, require illuminating a backlight panel, using a backlight source to light the screen, which results in additional energy loss.
Are LED displays energy-efficient?
As mentioned earlier, LED displays are inherently energy-efficient products, consuming less power than many electronic devices.
How can I further reduce LED display power consumption?
Installing LED displays with light sensors allows brightness adjustment based on ambient light levels, saving more energy. Additionally, promptly turning off the screen when not in use also conserves power.
Does voltage level affect LED display power consumption?
Voltage does influence power consumption. Excessively high voltage increases current flow through the display, thereby raising power usage.
While low voltage doesn’t directly increase power consumption, it causes the screen to dim, leading to flickering or failure to display properly.



