As 4K resolution becomes increasingly prevalent across display devices and video content, we encounter it virtually everywhere. Chances are, the computer monitor you’re using to read this article right now features 4K resolution. 4K resolution is precisely the subject we’ll explore in depth. Let’s delve into what 4K resolution is and why it matters so much.
What is resolution?
Resolution is essentially the product of the horizontal and vertical rows of pixels in a display device. It’s worth noting that in LED displays, pixels are replaced by LED light bulbs, so the product represents the number of LED bulbs in the horizontal and vertical rows.
What is 4K resolution?
Understanding resolution makes 4K resolution straightforward. It consists of approximately 4000 horizontal pixels. Note the use of “approximately” here, as the pixel count for 4K varies across different fields. Currently, 4K resolution primarily follows two specifications:
- Consumer use (e.g., TVs, LCD monitors, LED displays): 3840 x 2160 pixels
- Cinema: 4096 x 2160 pixels

Why are there two different 4K specifications?
From the perspective of display manufacturers, 3840 x 2160 pixels aligns perfectly with the 16:9 aspect ratio and can be easily extended as multiples of 2K, making it more memorable for consumers. However, cinemas produce films with an aspect ratio of approximately 1.90:1. Therefore, the resolution is appropriately increased to match this cinematic aspect ratio, resulting in a specification that differs from that used by display manufacturers.
4K Resolution: Advantages and Disadvantages
Although 4K resolution is now widely adopted with distinct advantages, it still has certain limitations. Let’s explore these further.
Advantages of 4K Resolution
Immersive Viewing Experience
4K resolution contains approximately 8.3 million pixels, the dense pixel density enables smoother transitions in images and videos, delivering exceptionally lifelike display quality.
Enhanced Image Clarity
At the same screen size, higher pixel density translates to sharper clarity. The difference becomes even more pronounced when comparing displays of different sizes. For instance, when exporting 4K JPG images from Adobe Photoshop, you may notice that despite sharing the same resolution, varying compression ratios yield significantly different levels of clarity and file sizes.
Integrated HDR Technology
Displays with 2K or 4K resolution typically incorporate High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology. This technology significantly enhances brightness in both the brightest and darkest areas of images or videos, revealing finer details with greater clarity.
Higher Refresh Rates
Whether LCD or LED displays, those manufactured at 4K resolution generally feature higher refresh rates than lower-resolution counterparts. This is because higher resolution demands more powerful chips, consequently boosting overall refresh rates.
Emerging as the Mainstream
With an increasing number of displays, videos, and streaming media produced in 4K resolution, it is steadily becoming the mainstream standard—awaiting replacement by the next innovative technology.
Disadvantages of 4K Resolution
Hardware and Software Demands
4K files place significant demands on computers. While standard machines can handle editing and rendering, performance is often sluggish and prone to stuttering. Furthermore, not all software supports 4K video operations, presenting considerable challenges for professionals who frequently edit and produce video content.
Increased Storage Space
Due to the greater data content required, 4K resolution files occupy substantially more storage space compared to lower-resolution video and image files.
Bandwidth Requirements
The larger file sizes of 4K multimedia formats necessitate higher bandwidth for viewing or transmission. In some developing countries, even 1080p resolution remains unsupported in many areas. For instance, even in economically advanced China, only a handful of video platforms support 1080p resolution, let alone the higher-resolution 4K experience.
Higher Costs
Take common displays as an example: upgrading from a 1080p monitor to a 2K monitor typically costs only about $50 more. However, upgrading from a 2K monitor to a 4K monitor can cost nearly double the price. For LED displays, upgrading from 2K to 4K resolution typically costs 2-3 times more. Therefore, opting for a lower resolution can be a smart way to achieve better value for money.

Comparing 4K Resolution to Other Resolutions
4K vs. HD
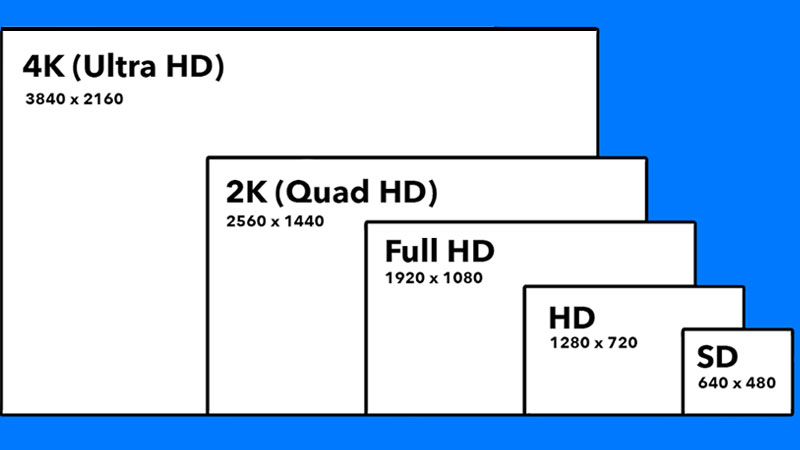
HD resolution is 1280*720px, hence it’s also called 720P. Compared to 4K, HD requires less storage space and lower computer specifications, making it still widely used today. In areas with slower internet connections, 720P loads significantly faster than 4K, making it the optimal viewing choice for many countries and regions.
4K Resolution vs.1080P Resolution
Based on 16:9 and 16:10 aspect ratios, 1080P offers two resolutions: 1920×1080px and 1920×1200px. To differentiate from HD, 1080P is commonly referred to as FHD (Full HD). 1080P resolution strikes a balance between clarity and compatibility, and its data volume is only one-fourth that of 4K resolution, making it the most commonly used resolution.
Due to the significant difference in pixel density between the two, there is also a substantial price gap. Many people are unsure how to choose between 4K and 1080P resolutions. Generally, if budget allows, it’s recommended to prioritize 4K resolution for its enhanced functionality and superior visual quality. If funds are limited, starting with a 1080P monitor is a viable option, with an upgrade considered later.
4K Resolution vs. 2K Resolution
2K resolution is 2560 x 1440, offering slightly higher clarity than 1080p while maintaining comparable pricing. Consequently, many users opt to upgrade their devices to 2K resolution.
Which Devices Support 4K Resolution?
TVs
As 4K TV prices continue to drop, 4K resolution has become the standard for televisions. After all, with prices not much higher than 2K TVs, 4K models offer significantly superior picture detail and sharpness. It’s like spending a little extra to get a much better product.
Laptops
4K resolution is a key selling point for many high-end laptops. If you pay close attention, you’ll notice “4K” prominently featured in promotional materials for numerous laptop models. This emphasis stems from the fact that many demanding games and advanced editing software perform better at 4K resolution. To meet the needs of this user base, premium laptops often feature 4K displays.
Monitors
Most average consumers aren’t familiar with monitor specifications like color gamut, panel type, or curvature. Therefore, more intuitive parameters such as size, brightness, and resolution become key purchasing criteria. To address this, many e-commerce platforms feature “resolution” as a filter option, helping users quickly find the monitor they want.
LED Displays
LED displays share a similar resolution calculation method with LCDs. However, as LED displays are custom-built products, the number of components required varies significantly across different resolutions. Consequently, upgrading an LED display from 2K to 4K resolution typically results in a substantial price increase.
Projectors
Among all display devices, projectors incur the highest cost per resolution upgrade. A standard 2K projector typically costs only $200–300, but upgrading to 4K demands $700–900—a full threefold increase. Given that the viewing experience doesn’t improve noticeably, projectors face far lower market demand compared to other categories.
Summary
In the consumer market, 4K resolution has gradually become mainstream due to its clear advantages and remains the optimal choice for most users. However, in streaming media transmission, the massive data requirements of 4K pose significant challenges for bandwidth and server infrastructure in most regions worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions About 4K Resolution
What’s the difference between 2160p and 4K resolution?
Historically, the vertical pixel count in a 16:9 aspect ratio is denoted by “P.” For example, 1280 x 720px is called 720P, and 1920 x 1080P is called 1080P. Applying this convention to 2160P, the formula 16/9 = x/2160 yields x = 3840. Therefore, 3840 x 2160 pixels equates to 2160P. This resolution is also known as 4K, meaning 4K resolution is synonymous with 2160P.
What is the pixel density of 4K resolution?
Multiplying 3840 by 2160 yields a pixel density of 8,294,400 for 4K resolution.
What is the maximum refresh rate for 4K resolution?
Refresh rates vary across different displays. Standard office monitors typically operate at 60Hz, while specialized gaming or visual effects monitors can reach up to 144Hz.
What is the recommended viewing distance for 4K resolution?
For LCD displays, the recommended viewing distance for 4K resolution is typically 1.5 times the screen size. For example, with a 55-inch TV: 55 (inches) × 1.5 × 2.54 (cm/inch) ≈ 2.1 meters. This translates to a recommended viewing distance of 2.1 meters.
For LED displays, the recommended viewing distance for 4K resolution is typically 1.5 times the LED module size. For instance, with an indoor LED display using P2 modules: 2 (module size) × 1.5 = 3 meters. Thus, the recommended viewing distance is 3 meters.
How does 4K streaming impact bandwidth usage? What is the recommended upload speed?
Compared to lower resolutions, 4K consumes significantly more bandwidth. For smooth 4K streaming, an upload speed of at least 50–100 Mbps is generally recommended. Otherwise, the video will experience noticeable buffering, negatively impacting the viewing experience.



