When selecting monitors, we often encounter two aspect ratios in specifications: 16:10 and 16:9. While their values appear very similar, what are the differences between 16:10 and 16:9, and how should we choose? Spend just 10–15 minutes reading this article, and you’ll feel confident navigating these two aspect ratios in the future.
First, let’s understand what aspect ratio means.
What is Aspect Ratio? What are the Width and Height for 16:10 and 16:9?
A screen aspect ratio is the ratio of a display device’s width to its height. Its meaning varies depending on the device type. For example, on an LCD monitor, 16:10 represents a width of 16 pixel units and a height of 10 pixel units. On an LED display, 16:10 signifies a width of 16 LED light beads and a height of 10 LED light beads.
Understanding the meaning of the 16:10 aspect ratio makes it easy to derive information about the 16:9 aspect ratio. The 16:9 aspect ratio is achieved by subtracting one unit of pixel width or one LED lamp height. Beyond this slight proportional difference, let’s explore further distinctions between the two.
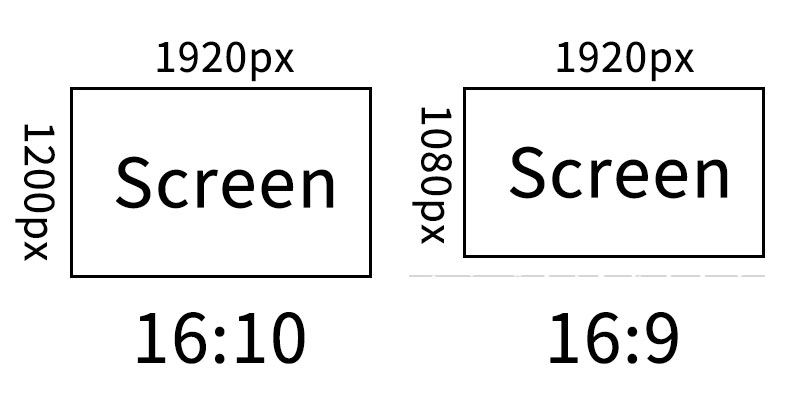
16:9 vs. 16:10: What are the differences?
16:9 vs. 16:10: Historical Context
Historically, 16:9 emerged much earlier than 16:10. The 16:9 aspect ratio became a standard for many HDTVs around the year 2000, while 16:10 gradually gained traction in computer monitors during the 21st century.
This shift primarily stemmed from computers’ role as productivity tools requiring greater information display. Increased vertical space allowed more content to be shown, enhancing work efficiency. However, during this period, 16:10 monitors remained cost-prohibitive and impractical for most users, remaining accessible only to a small segment of high-income individuals.
16:9 vs. 16:10: Screen Size
Screen size is primarily determined by manufacturers during device production. Since aspect ratios relate to the internal pixel count or LED array, screen dimensions do not dictate the aspect ratio manufacturers choose to implement. For example, a 16-inch laptop with a resolution matching 16:9 will have a 16:9 aspect ratio, while one configured for 16:10 resolution will feature a 16:10 aspect ratio. Only during actual use will you notice that a 16:10 screen displays slightly more content than a 16:9 screen of the same physical size.
Of course, some manufacturers slightly adjust the screen’s length and height to make the difference more visually apparent for consumers, as long as the final aspect ratio remains within the specified range. Using the 16-inch laptop as an example again, we’ve compiled an intuitive comparison table:
Comparison of 16-inch laptop diagonal and aspect ratios | ||
| Item | 16:9 screen | 16:10 screen |
| Diagonal | 40.64 cm | 40.64 cm |
| Width | 35.42 cm | 34.46 cm |
| Height | 19.93 cm | 21.54 cm |
| Features | Mainstream display ratio, ideal for entertainment, office work, etc. | The higher screen ratio makes it ideal for work. |
The listed dimensions reveal the screen size differences between the two formats. Visually, a 16:10 display appears slightly taller than a 16:9 model. The additional vertical space in 16:10 makes it ideal for multitasking with side-by-side windows, while 16:9 better accommodates various video and image formats, offering a more comfortable viewing experience.
16:9 vs. 16:10: Resolution
Having detailed the screen size comparison between 16:10 and 16:9, another key concern is their resolution performance. Looking at most popular monitors on the market, mainstream resolutions for 16:9 displays are 1920×1080px (1080P) and 3840×2160px (4K). In contrast, 16:10 displays lack a unified standard, with 2560×1600px and 1920×1200px being more common.
16:9 vs. 16:10: Content Compatibility
Having existed longer than 16:10, 16:9 has become the default aspect ratio for much content. Older applications or games may display a black bar at the bottom of 16:10 screens due to their higher resolution, or stretch the entire image, resulting in an awkward appearance.
For creators, the extra space means easier content handling. When using Adobe Photoshop or Adobe Illustrator for product layouts, web element design, etc., 16:10 often displays longer patterns and makes editing and moving images more convenient.
16:9 vs. 16:10: Popularity
Our observations reveal that people often hold preconceived notions. Since 16:9 has been around longer and is widely adopted across various devices, images, and films, users have grown accustomed to this aspect ratio. Consequently, when another ratio emerges, it struggles to match the accumulated user base and scale of adoption. From this perspective, 16:10 enjoys significantly less popularity than 16:9.
Additionally, multiple studies indicate that the human eye perceives 16:9 as the optimal viewing ratio. This is why screens with a 16:9 aspect ratio offer a more visually pleasing experience.
16:9 vs. 16:10: Pricing
Pricing is influenced by numerous factors, with volume being the most direct. Generally, higher production volumes lower overall costs and result in more competitive pricing. This is why many manufacturers promote “volume discounts.” This principle applies equally to 16:9 and 16:10 displays.
Due to the higher popularity and production volume of 16:9 displays, their prices are typically lower than those of 16:10 models. Currently, 27-inch 16:9 displays on the market range from $300 to $600, while 16:10 displays are slightly pricier, generally falling between $350 and $650.

16:10 vs. 16:9: How to Make the Best Choice?
After the detailed comparison above, we should now have a thorough understanding of the differences between these two aspect ratios. Next, let’s explore how to choose based on real-world application scenarios.
Entertainment (TV, Video, and Streaming)
For various entertainment purposes, 16:9 remains the optimal choice. Today, streaming platforms, television broadcasts, and video production all predominantly optimize content for the 16:9 aspect ratio. Moreover, 16:9 inherently accommodates common resolutions like 720p, 1080p, and 4K. Therefore, prioritizing a 16:9 monitor ensures the best visual experience.
Gaming
For newly released games, choosing either 16:10 or 16:9 displays poses no significant issues. Modern games are developed with full-screen display optimization across resolutions in mind. While the overall image may appear slightly stretched, the primary display elements show no noticeable distortion.
However, if you’re running older games or titles requiring emulators, these may not have been designed with cross-device compatibility in mind. Consequently, you might encounter issues like distorted visuals or black borders.
Productivity Applications
We’ve briefly outlined the productivity advantages of 16:10 above. Beyond image editing, fields like code development and data analysis—where displaying more data or information is crucial—benefit significantly from a 16:10 aspect ratio monitor.
Balancing Entertainment and Work
For those seeking to seamlessly blend entertainment and work, a compromise solution is prioritizing monitors with rotation capabilities. Many modern displays now support quick switching between landscape and portrait modes through rotation. This feature allows you to rotate the screen horizontally for video or gaming, and vertically for tasks like data analysis or image editing.
Conclusion
Overall, 16:9 offers broader compatibility and versatility than 16:10. For those balancing entertainment and work, a monitor with rotation capability is the solution. Of course, if your budget allows, consider purchasing two monitors with different aspect ratios.
FAQs
How do I check my computer’s aspect ratio?
For Windows computers: Navigate to Settings > System > Display. If the maximum resolution is 1920×1080, it’s 16:9. If the maximum resolution is 1920×1200, it’s 16:10.
For Mac computers: Check the resolution information under System Preferences > Displays. Note: Apple computers are not manufactured with 16:9 or 16:10 aspect ratios.
Can I change my monitor’s aspect ratio?
Yes, all computers support modifying the aspect ratio. However, you can only reduce the aspect ratio, not increase it. For example, a 16:10 computer typically has a 1920×1200 resolution, which can be changed to 1920×1080.
Does the aspect ratio affect image quality?
No, it does not. An image’s aspect ratio is a fixed format generated during software production. Therefore, the screen’s aspect ratio does not impact image quality. However, if the aspect ratio doesn’t perfectly match the display, viewing comfort may be slightly compromised.
Are 16:9 and 16:10 suitable for all display devices?
In most scenarios, 16:9 is a viable choice, while 16:10 may be more appropriate in certain contexts. However, neither format is universally applicable—many industrial displays, for instance, typically use a 4:3 aspect ratio.
What other common aspect ratios exist besides 16:10 and 16:9?
Beyond 16:10 and 16:9, ratios like 4:3, 21:9, and 32:9 are also widely used. 4:3 is often found in older devices or industrial displays, while 21:9 and 32:9 are typically employed for gaming or data analysis.



